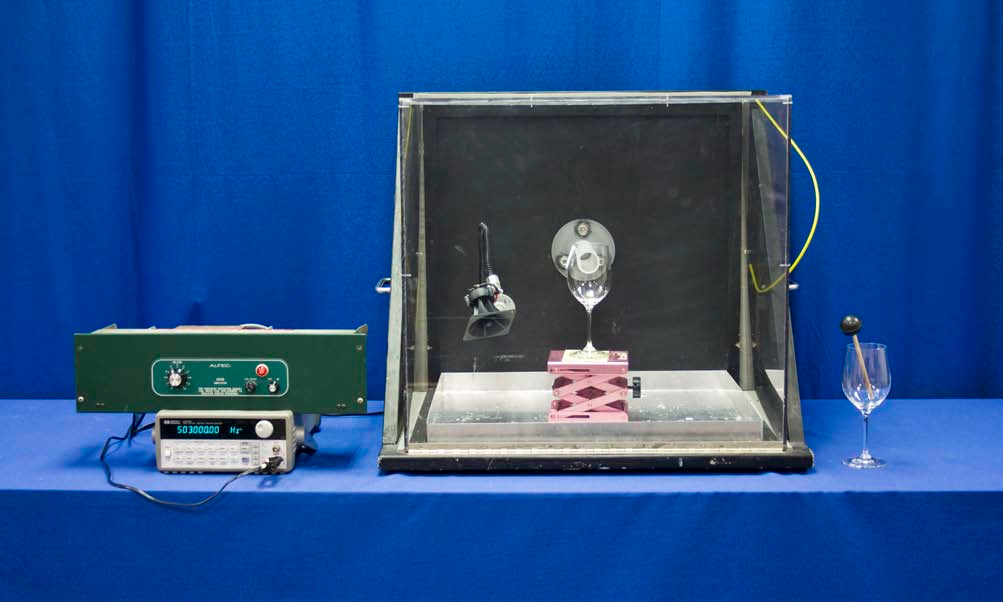


Concept
This classic demonstration of resonance uses intense sound waves whose frequency is tuned to match the natural frequency of a glass goblet. The glass has a high lead content, which produces the high quality factor, Q, required for this demonstration. The “quality” of the glass can be heard by noting how long it rings after tapping. The natural frequency of the particular goblet to be used is carefully measured before the demonstration to within ~ 0.1 Hz. When driven by the amplifier and speaker, the standing waves excited along the circumference of the goblet take about a second to build to maximum amplitude and break the goblet. It should be emphasized that frequency matching is crucial, and that no amplitude of a poorly matched audio signal will be sufficient to break the goblet.
Procedure
- Put the bent paper strip on the rim of the wine glass and place it on the lab jack stand right in front of the speaker tube as shown in the top-right picture. Close the protective Plexiglas cover.
- Turn on the amplifier (the red light will come on) and turn the volume down to 0.
- Turn on the function generator and set its amplitude to 700mV. Set its frequency to the predetermined resonance frequency written on the base of the glass (around 500Hz).
- Turn the volume up to about 7 on the amplifier and notice the vibration of the paper strip.
- Changing the frequency by 1 Hz at a time, notice the quick reduction in the amplitude of vibration of the paper strip when moving away from resonance.
- Move back to the resonance frequency and turn the amplifier volume up to maximum to break the wine glass. (If it doesn’t break, try searching for resonance more carefully or use the backup wine glass. DO NOT turn the function generator amplitude up beyond 700mA or you will break the speaker!)
Equipment
- Break the Glass Apparatus
- Amplifier
- Function Generator
- (2) Crystal Wine Glasses (High lead content, thin rim)
- Paper Strip
- Rubber Head Mallet