

Concept
This demonstration utilizes friction (rubbing) between two sources of different polarizability to remove or add electrons from one material and then transfer this excess charge onto the electroscope. The rubbing process typically scrapes off about $10^{10}$ surface electrons per mole of material, which may seem large, but in fact is only a tiny fraction of the total number of electrons, which is ~ $10^{24}$ or $10^{25}$ per mole. Although the polarities of the polycarbonate or PVC rod that result from rubbing are opposite to one another, the transfer of this charge to the electroscope produces, for both rods, the repulsion of the electroscope needle from the similarly charged main stem of the electroscope.
Procedure
- Verify that the electroscope needle is unlatched and free to move.
- Vigorously rub the polycarbonate rod with the felt to give the rod a positive charge.
- Hold the rod over (but not touching) the electroscope plate and notice that needle registers the charge strength.
- Repeat steps 1-3 using the PVC rod (the PVC rod will obtain a negative charge).
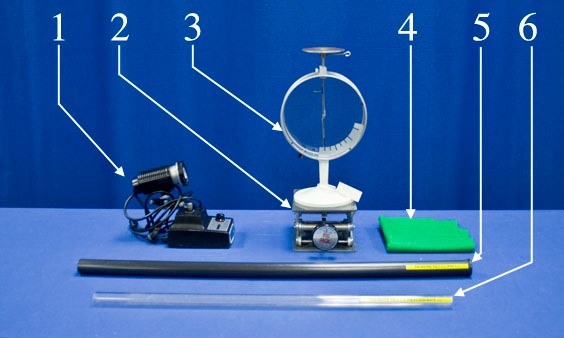
Equipment
- Spotlight
- Lab Jack
- Electroscope
- Polyester Felt
- PVC Rod
- Polycarbonate Rod